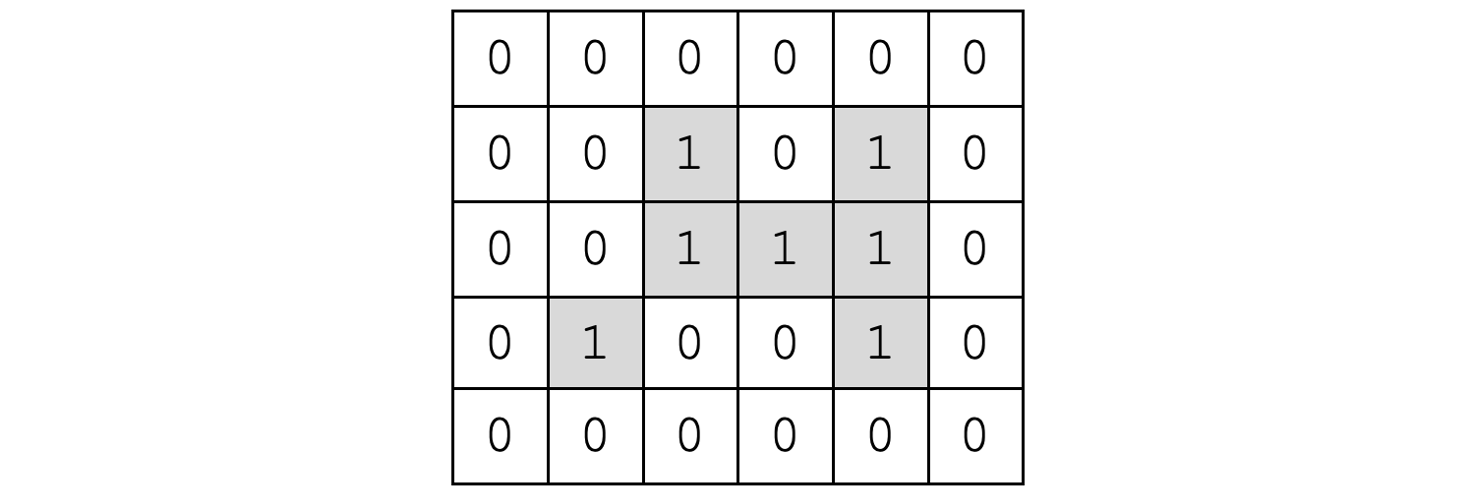
当前存在一个大小为m*n的二进制矩阵grid,假设岛屿是由一些相邻的1构成的组合,即两个1必须在水平或垂直的四个方向上相邻(假设grid外的位置全为0),岛屿的面积即岛上值为1的单元格的数目。计算并返回grid中最大的岛屿面积。若不存在岛屿,则返回面积为0。

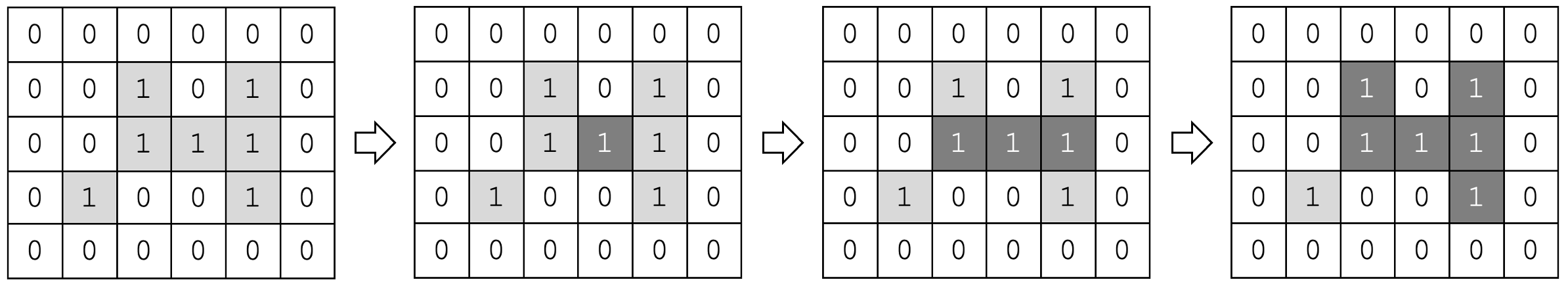
由于每个岛屿均被水包围,因此在登陆岛屿后,对岛上的每一寸土地进行递归即可计算当前岛屿面积,最后返回所有岛屿中所得的最大面积即可。登陆岛屿后的具体步骤为
以此时所处位置为中心,向上、下、左、右四个方向前进
若发现在该方向前进后抵达的新地点为水或为已抵达过的地点,则停止以该方向前进
若发现在该方向前进后抵达的新地点为未抵达过的地点,则在对其进行标记后,重复步骤1
此即深度优先搜索方法,该方法实际上将所抵达的点均压至栈中,当新入栈的点抵达边界条件时,该点会在执行完毕后出栈,直至栈被清空。而将执行操作的数据结构从栈替换为队列后,算法会转变为广度优先搜索方法,即每次执行操作时均从队首取出所储存的点,并将接下来需要遍历的点置于队尾,直至队列被清空。
DFS
在以grid中每一寸土地为中心进行递归前,需要确定边界终止条件,即遍历位置抵达grid的四个边缘外的时刻。其代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| int i, j;
if(i == grid.size() || i < 0){
return 0;
}
else if(j == grid[0].size() || j < 0){
return 0;
}
|
当所抵达的点为陆地时,需要将其标记为已抵达过的点,从而避免后续递归点再次对其进行遍历。因此,可将遍历后的点直接设置为0,此即著名的沉岛策略。尔后在对上、下、左、右四个方向上的地点进行递归,并同时统计该岛屿面积。加入边界终止条件后,其代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| int getProportion(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j){
if(i == grid.size() || i < 0){
return 0;
}
else if (j == grid[0].size() || j < 0){
return 0;
}
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
grid[i][j] == 0
return 1 + getProportion(grid, i + 1, j) + getProportion(grid, i - 1, j) + getProportion(grid, i, j + 1) + getProportion(grid, i, j - 1);
}
return 0;
}
|
尔后,通过主函数遍历grid中的每一个点,确定每个岛屿的面积大小,并实时更新最大岛屿面积,完整代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution{
int getProportion(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j){
if(i == grid.size() || i < 0){
return 0;
}
else if (j == grid[0].size() || j < 0){
return 0;
}
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
grid[i][j] == 0
return 1 + getProportion(grid, i + 1, j) + getProportion(grid, i - 1, j) + getProportion(grid, i, j + 1) + getProportion(grid, i, j - 1);
}
return 0;
}
public:
int maxProportionOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid){
int maxProportion = 0;
int proportion = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < grid.size();i++){
for(int j = 0;j < grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
proportion = getProportion(grid, i, j);
maxProportion = maxProportion < proportion ? proportion : maxProportion;
}
}
}
return maxProportion;
}
};
|
Python下代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
maxArea = 0
def getArea(x, y):
if not (0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0])):
return 0
if grid[x][y] == 1:
grid[x][y] == 0
return 1 + getArea(x - 1, y) + getArea(x + 1, y) + getArea(x, y + 1) + getArea(x, y - 1)
return 0
for m in range(len(grid)):
for n in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[m][n] == 1:
maxArea = max(getArea(m, n), maxArea)
return maxArea
|
BFS
首先建立队列,并设置操作执行过程中的终止条件。与DFS算法相同,该方法依旧采用沉岛策略,并根据队列顺序依次遍历岛屿中的点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| void getArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j){
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({i, j});
while(!q.empty()){
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = t.first, j = t.second, area = 0;
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i == grid.size() || j == grid[0].size()){
continue;
}
else if(grid[i][j] == 0){
continue;
}
grid[i][j] == 0;
area++;
if (i > 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == 1){
q.push({i - 1, j});
}
if (j > 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == 1){
q.push({i, j - 1});
}
if(i <= grid.size() && grid[i + 1][j] == 1){
q.push({i + 1, j});
}
if(j <= grid[0].size() && grid[i][j + 1] == 1){
q.push({i, j + 1});
}
}
}
|
尔后,建立主函数遍历grid中的每个点,其完整代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| class Solution{
public:
int area = 0;
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid){
int maxArea = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < grid.size();i++){
for(int j = 0;j < grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
area = 0;
getArea(grid, i, j);
maxArea = max(area, maxArea);
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
void getArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j){
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({i, j});
while(!q.empty()){
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i == grid.size() || j == grid[0].size()){
continue;
}
else if(grid[i][j] == 0){
continue;
}
grid[i][j] == 0;
area++;
if (i > 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == 1){
q.push({i - 1, j});
}
if (j > 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == 1){
q.push({i, j - 1});
}
if(i <= grid.size() && grid[i + 1][j] == 1){
q.push({i + 1, j});
}
if(j <= grid[0].size() && grid[i][j + 1] == 1){
q.push({i, j + 1});
}
}
}
};
|
Python下代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def getArea(grid, x, y):
queue = [[x, y]]
while queue:
[x, y] = queue.pop(0)
if 0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0]) and grid[x][y]:
grid[x][y] == 0
self.area += 1
queue += [[x - 1, y], [x + 1, y], [x, y + 1], [x, y - 1]]
return self.area
maxArea = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if(grid[i][j] == 1):
self.area = 0
maxArea = max(getArea(grid, i, j), maxArea)
return maxArea
|